Challenge
Insufficient digitalization level of outlet terminal domain equipment
The construction of new banking outlets requires the introduction of new terminal domain devices, such as STM, space capsule and interactive desktop. These devices often have high intelligent processing capability. However, the inherently closed design makes it very difficult to integrate with the platform domain or application domain. In addition, power and environment devices do not have direct digital presentation capabilities and can barely interface directly with the platform domain.
Complex platform domain scenarios with different requirements in northbound and southbound interfaces
In the construction of smart bank outlets, the platform domain is the key to both northbound and southbound interfaces. The southbound interfaces to the terminal domain, and needs to be compatible and open, with a unified standard, in order to facilitate the management of the subsequent increase in equipment. The northbound interfaces to the application domain. As a typical scenario of innovative applications, this needs to accommodate application developments aligned with diversified individual needs in the market. The different requirements for northbound and southbound interfaces bring great challenges in platform domain docking.
Varied equipment and data encoding formats bring difficulties when using the application domain
The business equipment, display equipment, security equipment, power and environment equipment, and other terminal domains of IoT device terminals greatly vary. That is, each manufacturer uses a different coding format. When accessing the platform domain, the data formats need to be unified for device management in the application domain above the platform.
Solution
Regardless of whether business equipment, display equipment or other devices with networking capabilities, or power and environment equipment that cannot be directly networked are used, the EMQ IoT data infrastructure can help achieve open standard protocol access to connect hundreds of millions of IoT devices in a flexible, scalable, secure and reliable manner. Thus providing the data foundation for smart banking digital business.
The cloud-native distributed IoT access platform EMQX is based on a powerful SQL-based IoT rules engine and data bridging, which can flexibly extract, filter, transform and process IoT data, and quickly integrate with more than 40 kinds of databases and enterprise systems, such as Kafka, SQL, NoSQL and time-series databases. This plays a crucial role in accelerating application integration and business innovation, improving network service capability, and creating sustainable competitiveness.
Relying on the capability of the EMQX Schema Registry, the data reported by the device domain can be processed, ensuring that the application domain receives a unified data format. In addition to supporting Avro, Protobuf and other common codec formats, this also supports custom coding to enable customized data format output. Thus greatly reducing the difficulty and time cost of data processing in application domains.
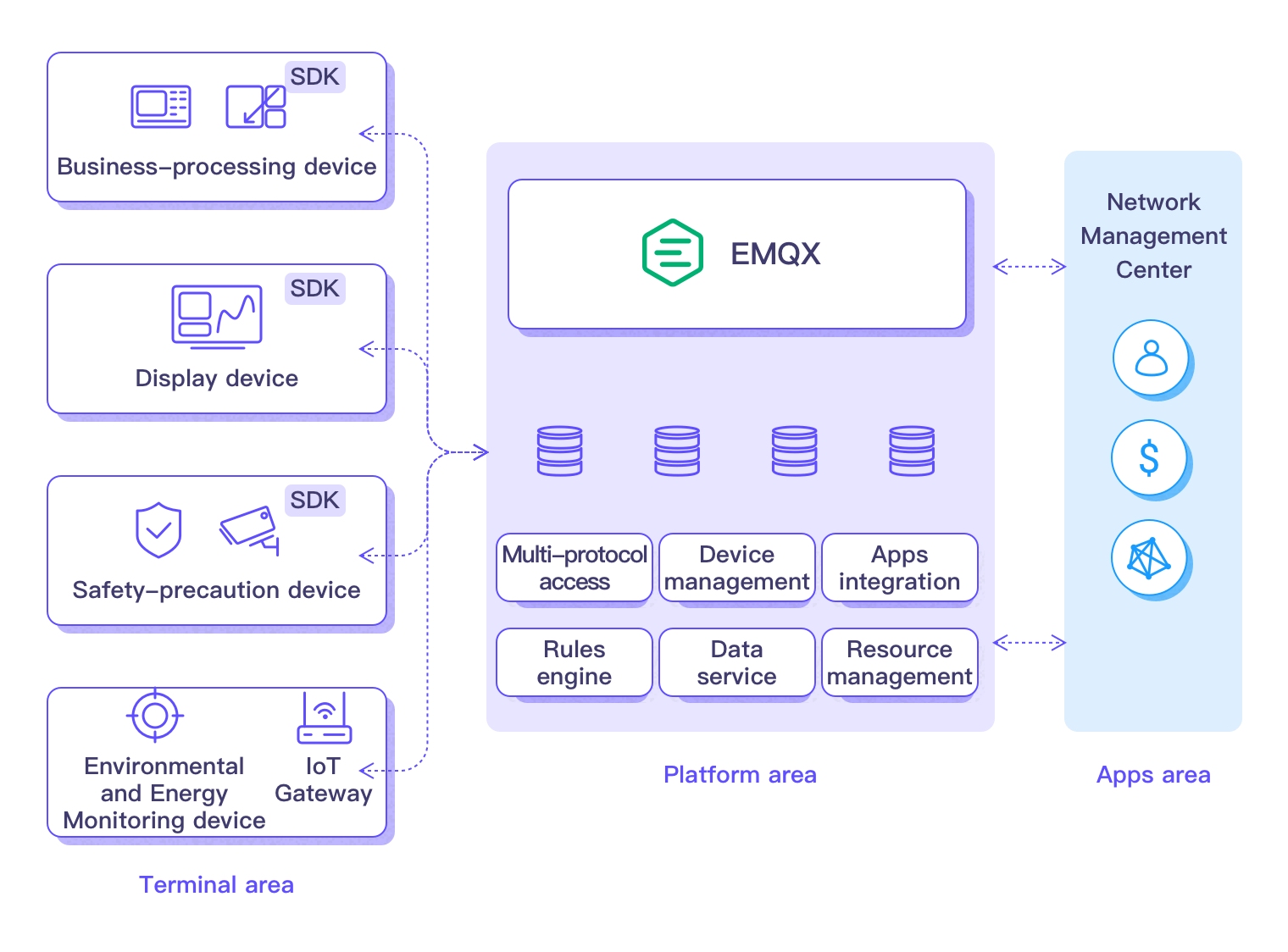
Results
- In the terminal domain, this realizes the digital access of various devices, diverse authentication mechanisms, perfect terminal authentication mechanisms, and other security solutions, in order to protect the security of financial services.
- In the platform domain and application domain, the rules engine is used to reduce the complexity of integration of traditional applications, realizing the implementation of IoT + Finance in a variety of scenarios. Thereby improving the digital service capability of outlets, enhancing customer experience, and creating more value for customers and enterprises alike.