MQTT Shared Subscriptions: Practical Guidelines and Use Cases | MQTT 5 Features

The Shared Subscriptions feature is introduced in MQTT 5.0 and widely used in production. Although this is a new feature of MQTT 5.0, MQTT 3.1.1 clients can use it as well. In this article, we will focus on shared subscriptions and dive into their mechanisms and use cases.
New to MQTT 5.0? Please check out our
What are Shared Subscriptions
In normal subscriptions, every time we publish a message, all matching subscribers will receive a copy. When a subscriber's consumption speed can't keep up with the message production speed, we cannot divert some of the messages to other subscribers to share the pressure. The performance issue of a single subscriber client could easily impact the entire messaging system.
MQTT 5.0 introduced Shared Subscriptions, which allow the MQTT server to evenly distribute message load among clients using a specific subscription. This means that when we have two clients sharing a subscription, each message that matches the subscription will only have one copy delivered to one of the clients.
Shared subscriptions bring not only excellent horizontal scalability to consumers, enabling us to handle higher throughput, but also high availability. Even if one client disconnects or fails, other clients sharing the same subscription can continue to process messages. When necessary, they can even take over the message flow that was originally intended for that client.
How do Shared Subscriptions Work?
With shared subscriptions, we don't need to make any changes to the underlying code of the clients. All we need to do is use topics that follow the naming convention when subscribing:
$share/{Share Name}/{Topic Filter}
$share is a reserved prefix, so the server knows this is a shared subscription topic. {Topic Filter} is the actual topic we want to subscribe to.
The middle {Share Name} is a string specified by the client, representing the share name used by the current shared subscription. Usually, the {Share Name} field is also referred to as Group Name or Group ID, making it easier to understand.
A group of subscription sessions that want to share the same subscription must use the same share name. So $share/consumer1/sport/# and $share/consumer2/sport/# belong to different shared subscription groups.
When a message matches the filters used by multiple shared subscription groups simultaneously, the server will choose a session from each matching shared subscription group to send a copy of the message. This is very useful when a topic's messages have multiple different types of consumers.
Even if two subscriptions have the same shared name {Share Name}, it does not mean they are the same shared subscription. Only {Share Name}/{Topic Filter} can uniquely identify a shared subscription group. The following subscription topics all belong to different shared subscription groups:
$share/consumer1/sport/tennis/+$share/consumer2/sport/tennis/+$share/consumer1/sport/#$share/comsumer1/finance/#
Shared subscriptions and non-shared subscriptions do not affect each other. When a message matches both a shared subscription and a non-shared subscription simultaneously, the server will send a copy of the message to each client of the matched non-shared subscription, and also send a copy to one session in each of the matched shared subscription groups. If these subscriptions are from the same client, then this client may receive multiple copies of the message.
Load Balancing Strategy of Shared Subscriptions
The core of shared subscriptions lies in how the server allocates message load among clients. Common load-balancing strategies include the following:
- Random: Randomly select a session within the shared subscription group to send the message.
- Round Robin: Send messages to the sessions in the shared subscription group in turn.
- Hash: Select a session based on the hash result of a field
- Sticky: Randomly select a session within the shared subscription group to send the message. Maintain this selection until the session ends, and then repeat this process.
- Local First: Randomly select, but prioritize sessions on the same node as the message publisher. If no such session exists, it degrades to a normal random strategy on the remote nodes.
The balance effects achieved by the Random and Round Robin strategies are relatively similar, so there is not much difference in their application scenarios. However, the actual balance effect of the Random strategy is often affected by the random algorithm used by the server.
In practical applications, messages may correlate. For example, multiple fragments belonging to the same image are obviously unsuitable for distribution to multiple subscribers. In this case, we need to choose a session based on the Hash strategy of Client ID or Topic. This ensures that messages from the same publisher or topic are always processed by the same session in the shared subscription group. Of course, the Sticky strategy also has the same effect.
The Local First strategy is more suitable for cluster use than the Random strategy. Prioritizing the selection of local subscribers can effectively reduce message latency. However, the premise of using this strategy is to ensure that publishers and subscribers are distributed fairly evenly on each node to avoid excessive differences in message load on different subscribers.
How do MQTT 3.1.1 Clients Use Shared Subscriptions?
Long before the release of MQTT 5.0, EMQX had designed a shared subscription scheme that many users have adopted. Similar to the official scheme of MQTT 5.0, EMQX recognizes the following format of topics as shared subscription topics in MQTT 3.1.1:
$queue/{Topic File}
The prefix $queue indicates that this is a shared subscription, and {Topic Filter} is the actual topic we want to subscribe to. It is equivalent to $share/queue/{Topic Filter} in MQTT 5.0, which means the share name is fixed as queue. So this scheme does not support multiple shared subscription groups with the same topic filter.
Since the naming convention of the shared subscriptions in MQTT 5.0, $share/{Share Name}/{Topic Filter}, is also a valid topic in MQTT 3.1.1, and the logic of shared subscription is implemented entirely in the MQTT broker, the client only needs to modify the topic content of the subscription. Therefore, even devices still using MQTT 3.1.1 can now directly use shared subscriptions provided by MQTT 5.0.
Shared Subscriptions Use Cases
Here are a few typical use cases for shared subscriptions:
- When the backend's consumption capacity does not match the message production capacity, we can use shared subscriptions to allow more clients to share the load.
- When the system needs to ensure high availability, especially for critical business with a large influx of messages, we can use shared subscriptions to avoid a single point of failure.
- When the influx of messages may grow rapidly in the future and the consumer side needs to be able to scale horizontally, we can use shared subscriptions to provide high scalability.
Suggestions for Using Shared Subscriptions
Use the Same QoS within a Shared Subscription Group
MQTT allows sessions within a shared subscription group to use different QoS levels, but this could result in different quality assurances when delivering messages to different sessions within the same group. Accordingly, debugging can become more difficult when problems arise. So it's best to use the same QoS within a shared subscription group.
Set Session Exirpy Interval Reasonably
It is common to use shared subscriptions together with persistent sessions. However, it's important to note that even if a client in a shared subscription group goes offline, as long as its session and subscription still exist, the MQTT server will continue distributing messages to this session.
Considering that the client may be offline for a long time due to failures or other reasons, if the session expiry interval is too long, many messages will be unable to be processed because they are delivered to the offline client.
A better choice might be to stop considering the subscriber when allocating message load once the subscriber goes offline, even if the session has not expired. Although this behavior is different from normal subscriptions, it is allowed by the MQTT protocol.
Demo
To better demonstrate the effect of shared subscriptions, we will use the MQTTX CLI, an MQTT command-line client tool, for the demonstration.
Start three terminal windows and use the following commands to create three clients connected to the Free Public MQTT Broker and subscribe to the topics $share/consumer1/sport/+, $share/consumer1/sport/+ and $share/consumer2/sport/+, respectively:
mqttx sub -h 'broker.emqx.io' --topic '$share/consumer1/sport/+'
Then start a new terminal window and use the following command to publish 6 messages to the topic sport/tennis. Here we use the --multiline option to send multiple messages each time we hit enter:
mqttx pub -h 'broker.emqx.io' --topic sport/tennis -s --stdin --multiline
The default load balancing strategy for shared subscriptions in EMQX is Round Robin, so we will see the two subscribers within the consumer1 group alternately receiving the messages we publish, while there is only one subscriber in the shared subscription group consumer2, so it will receive all the messages:
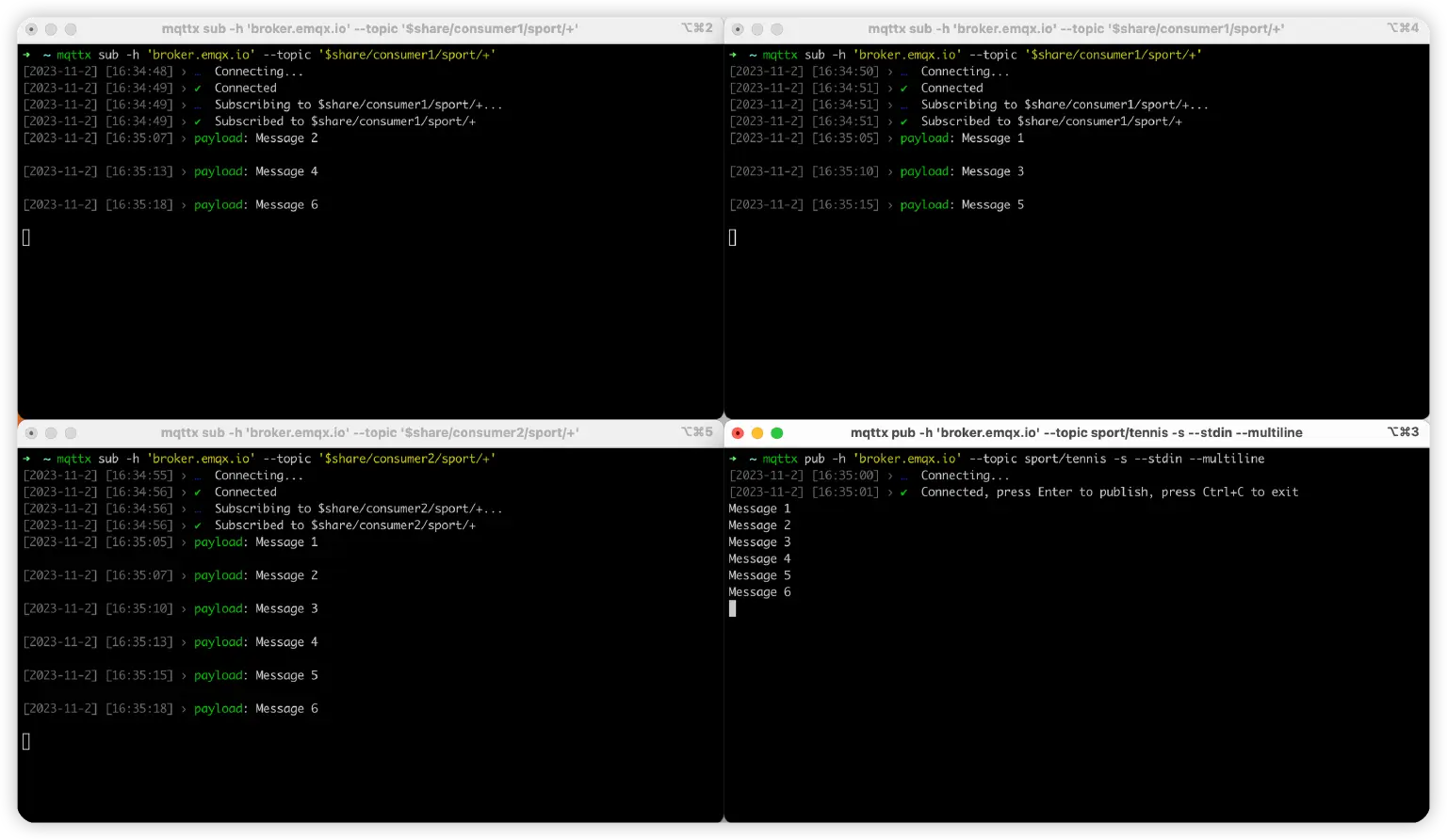
This is just a simple example. You can also try to join or leave the shared subscription group at any time, observe whether EMQX timely allocates the load according to the latest subscription, or install EMQX yourself and observe the behavior of different load balancing strategies.
If you want to know how to use the shared subscription feature in code, we provide Python example code in the emqx/MQTT-Features-Example project. This project aims to provide example code for all MQTT features to help everyone quickly understand how to use these features. We also welcome everyone to contribute more example code to this project.