Latency
Concurrent Connections
Messages/Second
Memory Footprint
IoT Data Hub at the Edge
EMQX Edge acts as the central data hub for a local site, factory, or facility. It aggregates data from all local devices (via Neuron or Kepware etc) and bridges it to the cloud.
Connect
Receives MQTT data from local devices or gateways like EMQX Neuron.
Process coming soon
Uses its rule engine to filter, transform, and route data locally.
Bridge
Publishes data via a secure, reliable MQTT bridge to a central cloud broker.
Your Lightweight Edge MQTT Broker
EMQX Edge is a full-featured MQTT broker that runs on-premise, handling local device communication and bridging critical data to the cloud.
Lightweight MQTT Brokering
Provides a full-featured MQTT 5.0 broker at the edge. Manage device-to-device communication, data streams, and local topic trees autonomously.
- Full MQTT 5.0 & 3.1.1 Support
- 100K+ Connections on a Single Node
- Runs on x86, ARM, and in Docker
Real-Time Data Processing
Use the SQL-based rule engine to process data in real-time. Filter noise, aggregate values, and transform data formats locally before bridging to the cloud.
- Intuitive SQL-like Syntax
- Trigger Local Actions & Alerts
- Reduce Cloud Data Costs
Seamless Cloud Bridging
Securely bridge selected data to any cloud platform. Synchronizes edge data with your central IT systems for a unified view and ensures data is never lost, even with unstable networks.
- Bi-directional Bridge to EMQX Cloud
- Connect to AWS IoT, Azure IoT Hub, etc.
- Automatic Buffering & Re-transmission
OPC UA & MQTT Integration
Combine the power of industrial protocols with MQTT. EMQX Edge acts as a local hub, receiving standardized MQTT data from OPC UA and Modbus (via Neuron) and bridging it to any MQTT platform.
- Integrate OPC UA & Modbus
- Aggregate edge data with MQTT
- Unified data model for IT/OT
Edge AI/ML Integration
Feed processed edge data directly into local AI/ML models. EMQX Edge's rule engine can trigger inference and publish results back via MQTT for real-time decision-making.
- Low-latency inference at the edge
- Real-time anomaly detection
- Optimize predictive maintenance models
Unified Namespace: Edge to Cloud
Seamlessly Integrate EMQX Neuron, Edge, and Cloud to build a unified namespace (UNS) architecture for your industrial data, enabling true IT/OT convergence.
Built for the Industrial Edge
EMQX Edge provides a robust, scalable, and secure broker for your edge to edge, and edge to cloud data pipeline.
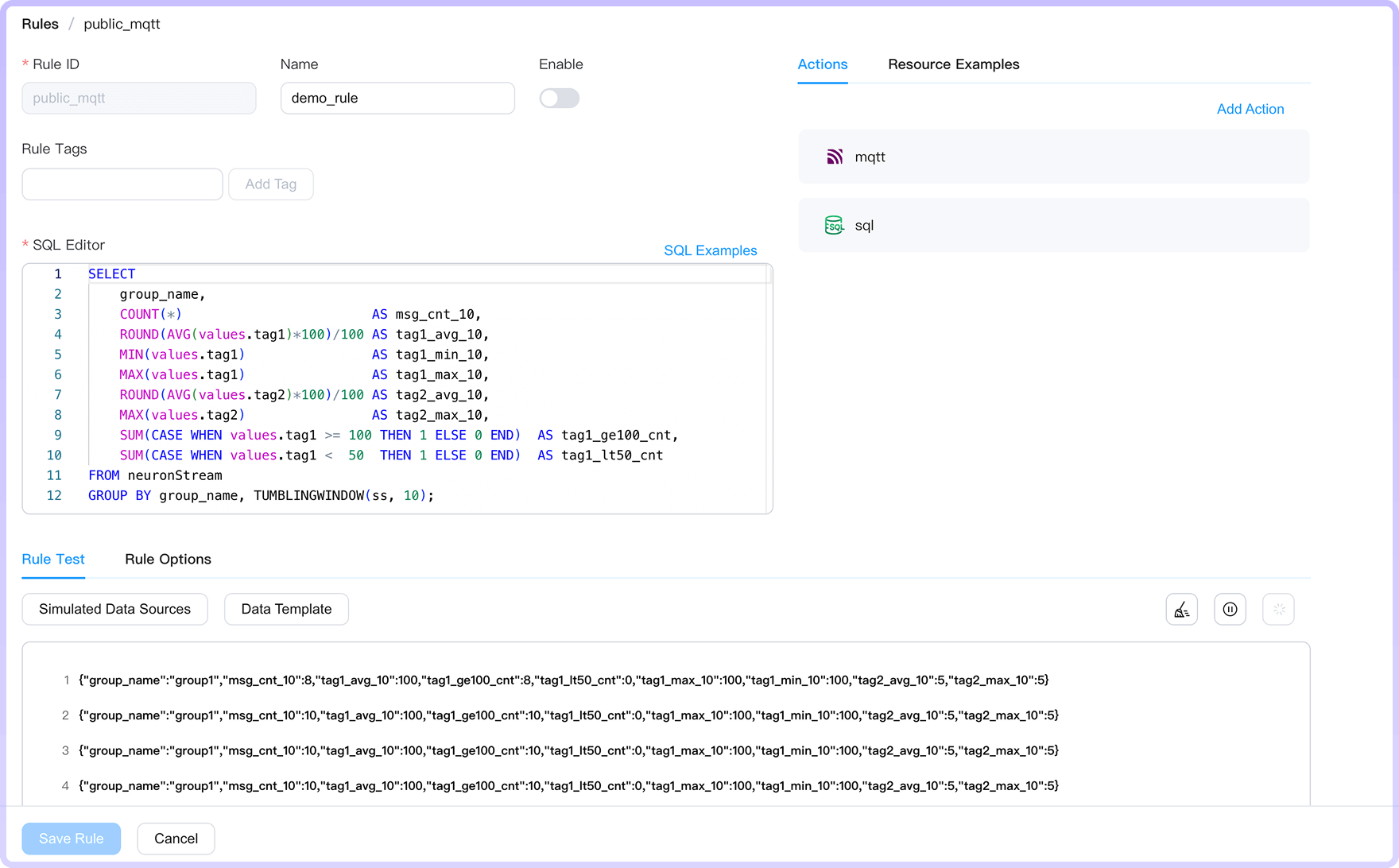
Process Data with a SQL-Based Rule Engine
Filter, transform, and route data locally with an intuitive SQL language, without writing complex code.

Powering Edge Industrial Scenarios
See how EMQX Edge is used across leading industries to manage edge data.

Factory Floor Data Hub
Deploy EMQX Edge as a local data hub on the factory floor. It aggregates data from multiple EMQX Neuron instances, manages local device communication, and bridges critical OEE data to the central MES/SCADA system.
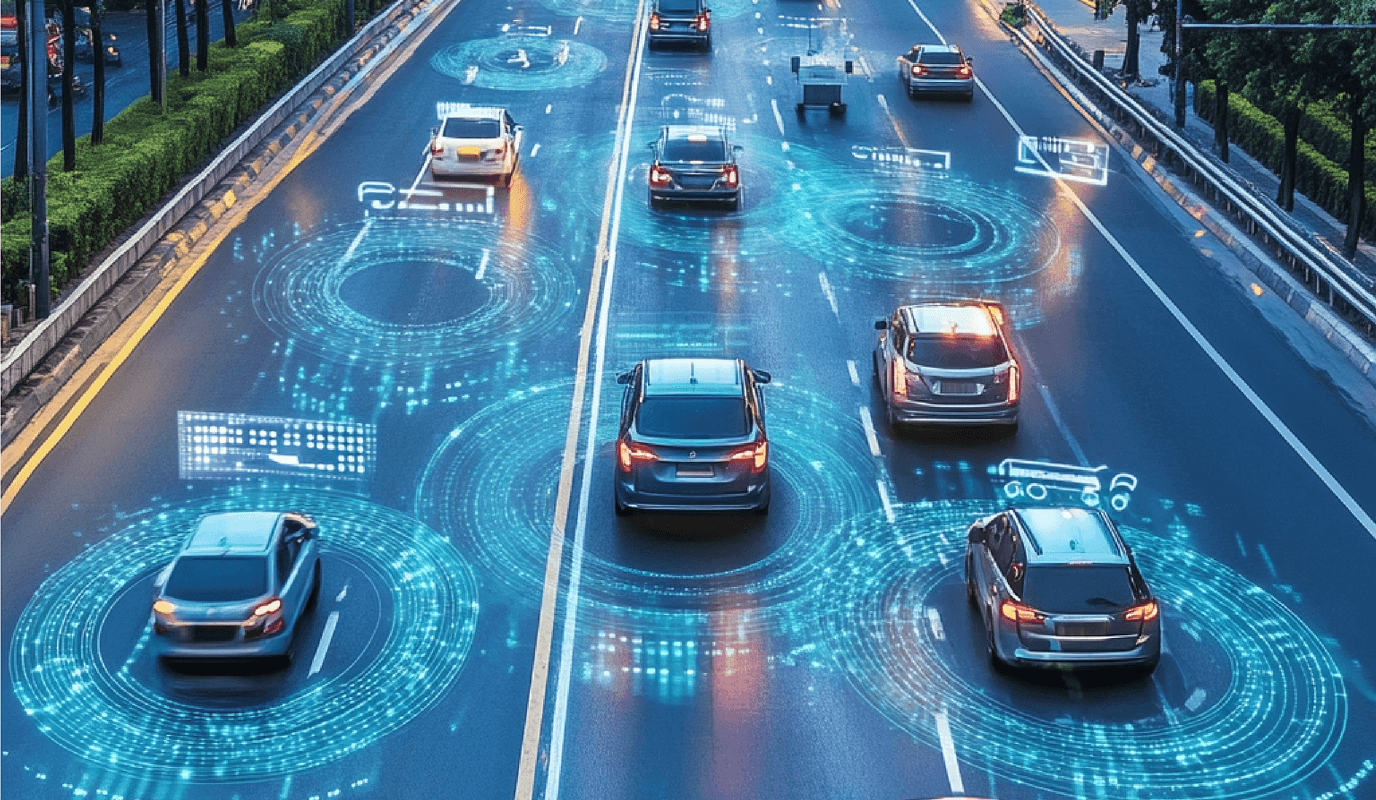
In-Vehicle Data Processing (T-BOX)
Run EMQX Edge on in-vehicle T-BOX units. It collects CAN bus data (via Edge extension), processes it in real-time for driver alerts, and uses the persistent bridge to send critical telematics to the cloud platform for fleet management.
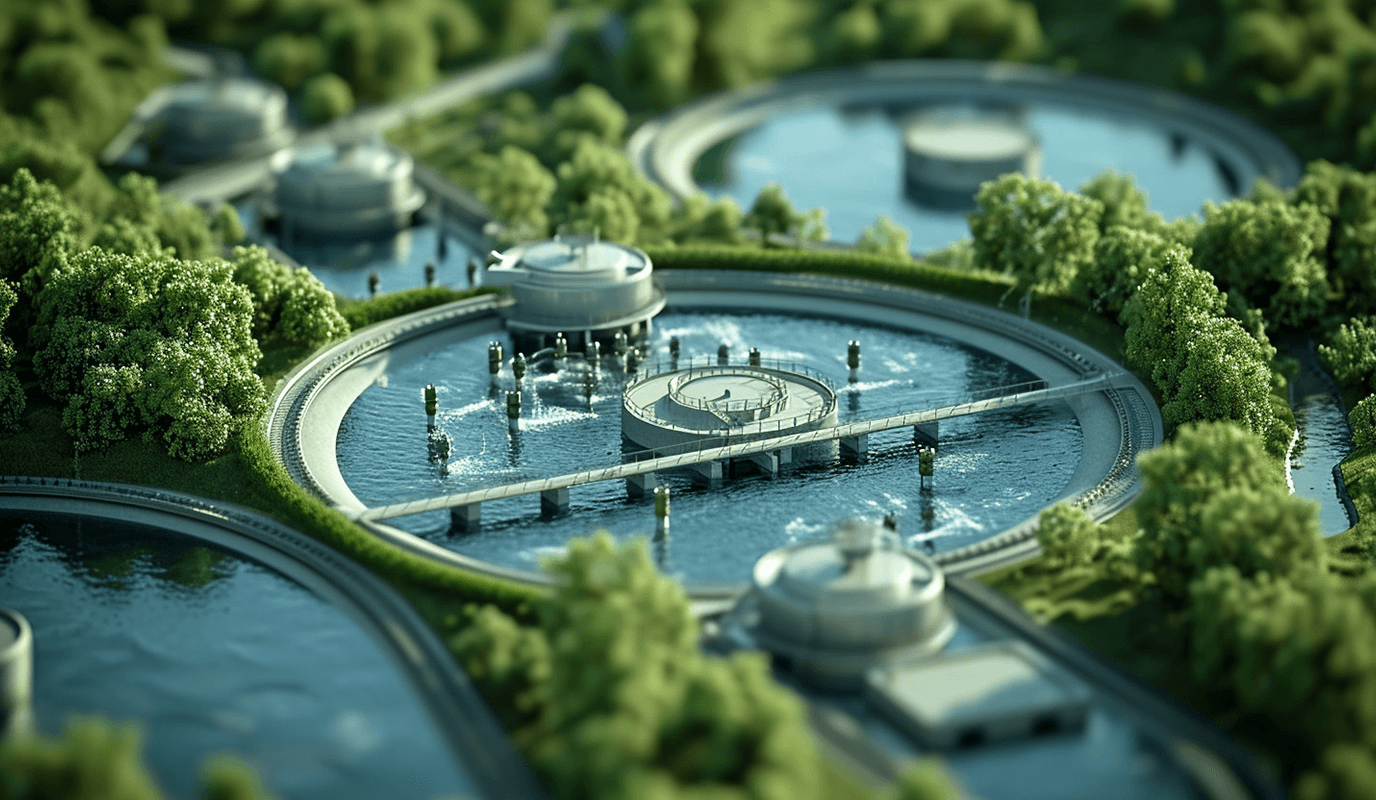
Smart Utility Data Aggregation
Install EMQX Edge on local data concentrators or gateways for smart meters, solar farms, or charging stations. It manages thousands of local device connections and securely bridges aggregated data to the central platform.
Frequently Asked Questions
Find quick answers to common questions about EMQX Edge.
Deploy Your Edge MQTT Broker Today
Download EMQX Edge for free and start processing your edge data in minutes. Have questions? Our experts are here to help.